X‑ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Using XPS to study the chemical composition of solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI)
Electrolyte reacts at the surface of charged electrodes, causing a buildup of electrolyte decomposition products. This layer of decomposition products is known as the “solid-electrolyte interphase” (SEI). The SEI strongly influences the lifetime of the cell. Understanding the chemical nature of the SEI allows insight into the chemical reactions which cause cell failure and improves the understanding of the effect of beneficial electrolyte additives.
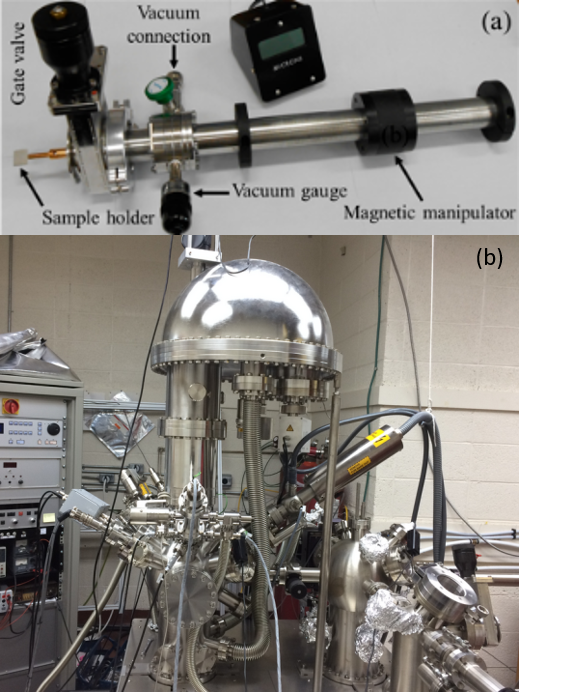
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)isВ aВ highly sensitive techniqueВ forВ identifyingВ andВ quantifyingВ theВ chemical statesВ of elements on the outermost surface of a solid. It is especially useful for determining the chemical composition of thin films, such as the SEI. Using a specially designed, air-tight “suitcase”, shown in Figure 1a , samples of aged electrodes can be transferred, without exposure to air, into the XPS system, shown in Figure 1b.В
- L. Madec, J. Xia, R. Petibon, K. J. Nelson, J.-P. Sun, I. G. Hill, and J. R. Dahn, J. Phys. Chem. C, 118, 29608–29622 (2014).
- L. Madec, R. Petibon, J. Xia, J.-P. Sun, I. G. Hill, and J. R. Dahn, J. Electrochem. Soc., 162, A2635–A2645 (2015).
- R. Petibon, L. Madec, L. M. Rotermund, and J. R. Dahn, J. Power Sources, 313, 152–163 (2016).
